the core tools in Google Ads for pinpointing your ideal audience. It covers Customer Match, which uses first-party data like emails to target existing or similar customers; Audience Segmentation, including Affinity, In-Market, Demographics, and Life Events to create precise audience groups; and First-Party Data Strategy, emphasizing CRM, app, and offline data to enhance targeting in a privacy-focused, post-cookie era.
Partnering with a AdWords agency Dubai can help you implement these strategies effectively, ensuring that your ads reach the right people at the right time.
Table of Contents
Now, let’s dive into the subsequent sections as outlined in your structure:
Define Your Customers with Google Ads Advertising
Imagine pouring your ad budget into a campaign that reaches everyone but connects with no one. That’s the risk of skipping customer definition in Google Ads. Pinpointing your audience isn’t just a checkbox—it’s the backbone of campaigns that convert. When you know who your customers are, every ad dollar works harder, driving higher click-through rates, better conversions, and a stronger return on investment (ROI). Without this focus, you’re casting a wide net and hoping for luck, which rarely pays off.
Google Ads gives you the tools to move beyond guesswork. By defining your customers based on their interests, behaviors, and demographics, you can craft ads that feel personal and relevant. Whether you’re running a global campaign or focusing on Google Ads Optimization Dubai, these strategies help ensure your campaigns hit the mark every time.
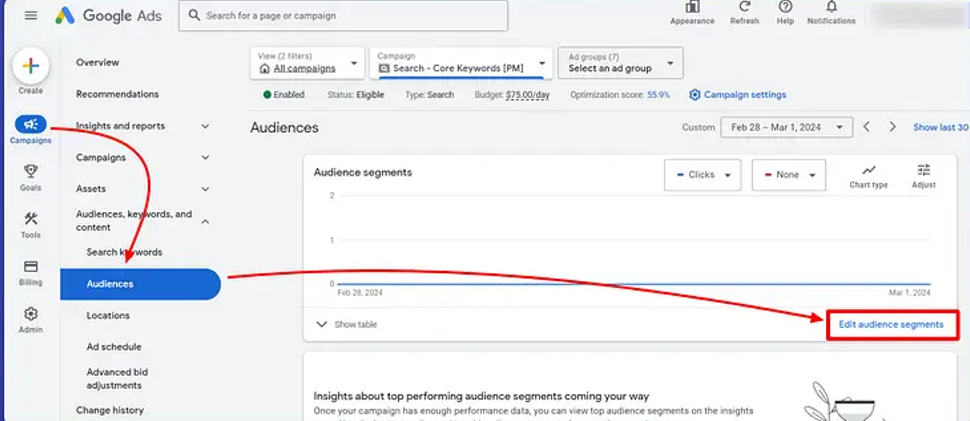
Define Customers with Google Ads Customer Match
Customer Match is like having a direct line to your most valuable customers. It lets you upload first-party data—think email addresses or phone numbers from your CRM—and target those users across Google’s network, including Search, YouTube, and Display. You can also find new customers who share traits with your existing ones.
How it works:
Upload a secure list of customer data, and Google matches it to user profiles. Use these matches to show tailored ads or build lookalike audiences.
Best practices:
- Segment lists by behavior (e.g., frequent buyers vs. one-time purchasers).
- Keep data fresh—update lists regularly to avoid outdated contacts.
- Pair with personalized ad copy to boost engagement.
For example, a local gym could upload a list of past members to offer a “come back” discount, rekindling interest with precision.
Use Audience Segmentation in Google Ads
Google Ads offers a toolbox of audience segments to narrow your focus. From broad interests to specific purchase intent, these segments help you reach the right people at the right time.
Key segment types:
- Affinity Audiences: Target users based on long-term interests, like “fitness buffs” or “tech enthusiasts.”
- In-Market Audiences: Reach people actively researching products, such as “in-market for home appliances.”
- Detailed Demographics: Filter by age, gender, income, or parental status.
- Life Events: Connect during milestones like moving or getting married.
- Building custom segments: Combine search terms (e.g., “best running shoes”) and visited URLs to target niche groups with high intent.
- Pro tip: Use keyword-driven segments for Search campaigns and URL-based signals for Display to align with user behavior.
A pet store, for instance, could target “dog owners” (demographic) who are “in-market for pet supplies” (intent) to promote a new line of organic dog food.
Defining Customers with First-Party Data Strategy
With third-party cookies fading, first-party data is your golden ticket. It’s the information you collect directly from customers—website visits, app activity, or even offline purchases. This data fuels precise targeting while keeping you compliant with privacy laws.
Why it matters:
- First-party data builds trust and relevance in a post-cookie world.
How to use it:
- Sync CRM data to retarget past buyers with upsell offers.
- Track app interactions to target engaged users.
- Use offline data (e.g., in-store purchases) to bridge online and physical touch points.
Stay ethical:
- Be transparent about data collection and comply with GDPR, CCPA, or other regulations.
A coffee shop chain could use loyalty program data to target frequent customers with ads for a new seasonal drink, ensuring relevance and boosting repeat visits.
Advanced Targeting Strategies to Define Customers in Google Ads
in Google Ads explores sophisticated methods to refine audience targeting. It covers Combine Segments to Build Hyper-Targeted Audiences, which layers demographics, interests, and behaviors for precise targeting; Attract New Customers with Acquisition-Focused Targeting, focusing on new prospects with tailored ads and cost-effective strategies; and Expand Reach with Similar Audiences (Lookalike Audiences), using first-party data to find new users who mirror your best customers, ideal for scaling campaigns.
Let me know if you want me to proceed with explanations for the remaining sections or focus on something specific!
Combine Segments to Build Hyper-Targeted Audiences
Layering audience segments is like crafting a custom recipe for your ideal customer. By combining demographics, interests, and behaviors, you create hyper-targeted groups that are more likely to convert.
How to combine:
- Use AND logic for precision (e.g., “parents AND in-market for baby products”).
- Use OR logic to broaden reach (e.g., “travel enthusiasts OR in-market for flights”).
Real-world examples:
- Ecommerce: Target “women aged 25-34” + “in-market for skincare” to promote a new moisturizer.
- B2B: Reach “business owners” + “searched for cloud software” to pitch a SaaS tool.
A travel agency could combine “parents aged 30-45” with “searched for family vacations” to advertise kid-friendly resorts, hitting a sweet spot for relevance.
Attract New Customers with Acquisition-Focused Targeting
New customer acquisition goals in Google Ads help you find fresh faces while keeping costs in check. These campaigns prioritize users who haven’t interacted with your brand yet.
Setup tips:
- Enable “New Customer Acquisition” in campaign settings.
- Craft ad copy that speaks to first-time buyers (e.g., introductory offers).
- Optimize landing pages for trust—clear CTAs, testimonials, and easy navigation.
Balancing act:
- Weigh acquisition costs against customer lifetime value to ensure profitability.
A subscription box service could target “in-market for beauty products” with a “first box free” offer, enticing new subscribers without overspending.
Expand Reach with Similar Audiences (Lookalike Audiences)
Similar Audiences (or Lookalike Audiences) let you scale your reach by targeting users who mirror your best customers. Google analyzes your first-party data to find new prospects with similar behaviors.
How it’s built:
- Start with a seed list (e.g., past purchasers), and Google identifies users with matching traits.
Best use cases:
- Display ads to build brand awareness.
- YouTube campaigns to engage visually.
- Discovery ads for mobile-first audiences.
Integration tip:
- Pair with broad creative to test what resonates with new segments.
A fitness app could use a list of active subscribers to find lookalike users, promoting a free trial to people likely to stick around.
Optimize Campaigns Based on Customer Definitions
focuses on refining Google Ads campaigns using audience insights. It covers Behavioral Data-Driven Optimization, leveraging user journey data from Google Ads and GA4 to adjust segments and messaging; A/B Testing for Customer Segmentation Accuracy, testing demographics, devices, and timing to validate targeting; and Machine Learning for Predictive Targeting, using tools like Smart Bidding and Performance Max to predict high-value audiences while maintaining control. if your ads aren’t delivering due to account-level issues, consider starting with an AdWords account recovery to regain full performance.
Let me know if you’d like me to explain the remaining sections or dive deeper into anything specific!
Behavioral Data-Driven Optimization
Understanding how users move through your funnel is key to refining your audience. Google Ads and Google Analytics 4 (GA4) provide rich behavioral data to guide your strategy.
What to track:
- Page views and time spent to gauge interest.
- Cart additions or form submissions to spot intent.
- Drop-off points to identify friction.
How to act:
- Redefine segments based on triggers (e.g., “visited pricing page but didn’t convert”).
- Tailor ads to funnel stages—awareness, consideration, or decision.
An online bookstore could retarget users who browsed fiction but didn’t buy, offering a discount to nudge them toward purchase.
For advertisers in the region, solid Google Ads management UAE practices ensure these optimizations lead to measurable results.
A/B Testing for Customer Segmentation Accuracy
A/B testing ensures your audience segments are on point. By experimenting with different targeting criteria, you can fine-tune who sees your ads.
What to test:
- Demographics (e.g., age 18-24 vs. 25-34).
- Device types (mobile vs. desktop).
- Ad scheduling (weekdays vs. weekends).
How to analyze:
- Compare click-through rates, conversions, and cost per acquisition to spot winners.
Next steps:
- Narrow segments that perform best or expand to test new hypotheses.
A tech retailer could test “in-market for laptops” on mobile vs. desktop, discovering mobile users convert faster and adjusting bids accordingly.
Machine Learning for Predictive Targeting
Google’s machine learning takes the guesswork out of targeting. Tools like Smart Bidding, Performance Max, and Optimized Targeting predict who’s most likely to convert.
When to use:
- Smart Bidding for automated bid adjustments.
- Performance Max for cross-channel reach.
- Optimized Targeting to discover unexpected segments.
Stay in control:
- Monitor ML suggestions and exclude irrelevant audiences to avoid drift.
Pro tip:
- Use conversion tracking to feed accurate data into Google’s algorithms.
A home decor brand could use Performance Max to find new buyers, letting Google’s AI uncover segments like “recent movers” automatically.
Key Practices for Defining Customers with Google Ads
Keep audiences fresh:
- Update lists monthly to reflect new behaviors or purchases.
Align teams:
- Ensure marketing, sales, and support share the same buyer personas for consistency.
Prioritize privacy:
- Be upfront about data use and follow regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
Avoid over-segmentation:
- Too many narrow segments can limit reach—aim for a balance.

Comparing Google Ads Audience Targeting Methods
| Targeting Method | Data Source | Benefits | Challenges |
| Customer Match | First-party data | High precision, personalization | Requires clean user data |
| Similar Audiences | Google’s algorithms | Scalable reach with similar behavior | Less control, performance varies |
| Custom Segments | Search behavior, URLs | Customizable based on intent | Needs ongoing refinement |
| In-Market Audiences | Browsing behavior | High purchase intent | Broader, less specific |
| Affinity Audiences | Lifestyle interests | Great for brand awareness | May be too broad for direct sales |
Conclusion: Turn Insight into Action by Defining Customers with Google Ads
Defining your customers isn’t just a step in Google Ads—it’s the foundation of campaigns that deliver. Whether you’re a small business or a global brand, mastering audience targeting unlocks better results, higher ROI, and lasting growth. Use tools like Customer Match, audience segmentation, and machine learning to connect with the right people at the right time. Stay agile, test often, and let data guide your path to success.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I define the right customers using Google Ads?
Start with Customer Match to target known users, then layer custom segments using search terms and behaviors. Combine data like age, interests, and intent for precision.
What’s the difference between In-Market and Affinity audiences in Google Ads?
In-Market audiences are ready to buy, actively researching products. Affinity audiences have long-term interests, making them ideal for building awareness.
Can I use offline data to define audiences in Google Ads?
Absolutely. Customer Match lets you upload offline CRM data, like emails or phone numbers, to target existing customers or find similar ones online.



